Keyword [Cerebral Blood Flow]
Ulas C, Tetteh G, Kaczmarz S, et al. DeepASL: Kinetic Model Incorporated Loss for Denoising Arterial Spin Labeled MRI via Deep Residual Learning[C]//International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Springer, Cham, 2018: 30-38.
1. Overview
1.1. Motivation
Arterial spin labeling (ASL) allows to quantify the cerebral blood flow (CBF) by magnetic labeling of the arterial blood water, but suffers from an inherently low-signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
In this paper
- FCN to learn residual from noisy perfusion-weighted image
- incorporate the CBF estimation model in the loss function during training
1.2. Model
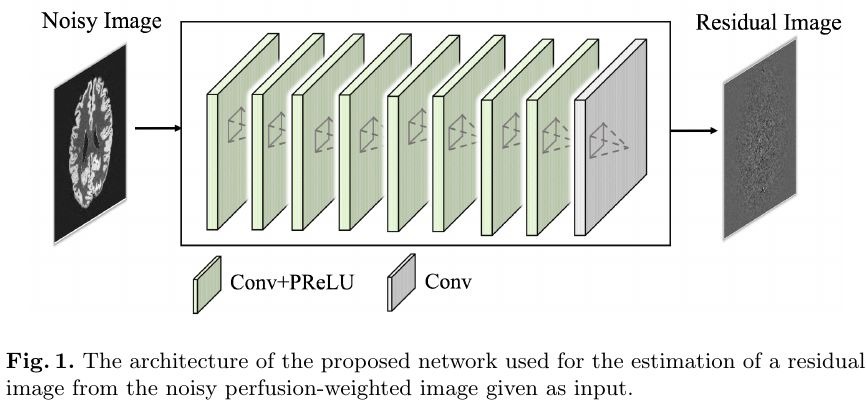
- Input. 2D noisy gray image patches
- 8 Conv2D (48 channels, 3x3, following pReLU) + 1 Conv2D (no activation)
- training. 18000 patch pairs of 40x40, batch size 500, 200 epoch, LR 0.0001
1.3. CBF Estimation Model

- β. brain-blood partition coefficient
- T_{1b}. longitudinal relaxation time of blood
- α. labeling efficiency
- τ. label duration
- PLD. post-label delay
- SI_{PD}. proton density weighted image
- ΔM. perfusion-weighted images
1.4. Loss Function

- N. noisy
- f_t. reference CBF value for each voxel
1.5. Experiments
